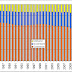
The Managing Health Care Costs Indicator is 25%
Atul Gawande has an essay in the August 2
New Yorker magazine about end of life care.
Gawande marvels that we physicians encourage patients to get obviously futile care – and that the care we give people at the end of their lives is part of the cause that health care has gotten so expensive. He gives examples from his own practice where he’s had a hard time telling patients there is no hope.
He goes out to a patient visit with a hospice nurse, and reports that she corrected him when he suggested that the purpose of hospice was to “let nature take its course.”
The hospice nurse defined the point as to helping patients “live the fullest life now.”
People often note that a quarter of Medicare dollars are spent on the last six months of life. That's the source of today's indicator. It turns out that while end of life care is a big cost driver for Medicare, it is a much smaller cost driver for employer-based health insurance plans.
I’ve been doing a bunch of thinking about end of life care lately.
We all know anecdotally that we offer futile care – and we all know further that flogging people as they are dying leads to more pain and suffering for the person dying, and for all of their loved ones.
We also understand that there is ridiculous variation in the way care is delivered to those at the end of their lives. Here's data from Dartmouth researchers published in Health Affairs in 2004.
Of course, the biggest cost of futile care is non-financial, and is borne by dying patients and their families, who bear unnecessary pain and suffering, and are robbed by medical technology of the chance to say goodbye.
On the other hand…
People at the end of their lives sometimes find every “found” minute precious. Healthy people doubt how much suffering they would be willing to endure to live a few more days or weeks. Sick people often, not always, would endure hell to breath a bit longer. So who are we to say otherwise?
There was a haunting article in the
New York Times in April about a palliative care specialist who was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 31, and who helped guide hundreds of her patients to a “better” death during her career.
….As the doctors began to understand the extent of her underlying cancer, “they asked me if I wanted palliative care to come and see me.”
She angrily refused. She had been telling other people to let go. But faced with that thought herself, at the age of 40, she wanted to fight on.
My colleague Jaan Siderov, in the excellent
Disease Care Management Blog points out that he saw patients who were at death’s door in the ICU – and who said “Surprised to see me, Doc?” when they came to his office for post-discharge followup.
There is certainly a lot of cost associated with end of life care.
People get
Folotyn for their non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and the cost is $30,000 per month and there’s been no proof of even life extension.
On the other hand I was talking about this to a colleague whose wife has non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
It’s a different discussion entirely.
There is no easy answer here. From a health policy point of view, I know that when we treat someone with an expensive drug who has no hope of benefit, there are fewer resources available in health care to immunize kids or counsel those at risk for sexually transmitted disease. Further, I know that societally we’ll have fewer resources to fix the roads and provide good educations to our kids. From a human point of view, though, I understand why people cling to the tiniest of hopes, even in the shadow of irrefutable evidence that these hopes are false.
What should we do?
Let’s learn from
Oregon and
Washington state.
They’ve each instituted the
POLST (Physician Order for Life Sustaining Treatment) to allow patients to designate that they don’t want resuscitation if they stop breathing or their hearts stop.
Let’s learn from Lacrosse,
Wisconsin, where few nursing home residents are transferred to the hospital – and a majority of elderly residents have advance directives.
85% of those who died had a living will.
85%!
In most communities, it is well under fifty percent.
Let’s talk to our loved ones about what kind of care they would want if they were unimaginably sick. Let’s not wait until they have tubes in every orifice, and we can’t talk to them. Let’s tell our loved ones what we want for ourselves, too.